
Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Une méthode simple pour quantifier objectivement la force musculaire des rats et souris et...

La roue d'activité spontanée BIOSEB offre une solution efficace pour quantifier l'activité...

La Roue Instrumentée pour Exercice Spontané est une méthode simple pour mesurer l'activité...

Une façon simple pour mesurer l'activité des rongeurs sur plusieurs jours dans leurs cages de...

Conçu pour les études sur l'entraînement physique et la fatigue chez les rongeurs - et désormais...

Instrument de test de la sensibilité de l'animal à la douleur résultant de l'exposition à la...

Un test indépendant de l'opérateur pour étudier les seuils de douleur chez les rongeurs (rats et...

Le Test de Gradient Thermique indépendant de l'opérateur est un nouvel instrument de recherche...

Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur...

Test non douloureux pour mesurer le niveau d'inconfort (incapacitance) de petits animaux comme...

Un instrument unique qui ne fournit pas seulement la mesure indépendante et automatisée du poids...
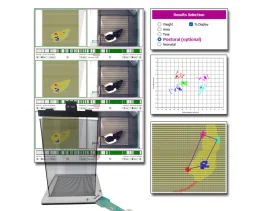
Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés Le système de...

Une solution rapide pour déterminer le seuil de sensibilité à la douleur mécanique chez les...

En tant que version électronique du classique esthésiomètre à filaments de Von Frey, la...

Nouvelles cage de contention modulables ROBUSTES pour maintenir doucement les rongeurs (rats et...

Une solution économique et versatile pour les situations nécessitant des tests sensoriels...

Dédié aux petits animaux tels que les rats et les souris, le Smalgo est un algomètre (ou...

La version 5 du Test de Suspension Caudale de Bioseb, basée sur des capteurs de force ainsi que...

NOUVEAU ! Solution complète (matériel et logiciel), dédiée et automatisée pour le Labyrinthe...

Un nouveau système innovant pour l'automatisation du test d'Open Field pour rats et souris:...

Test open-field - ARENE UNIQUEMENT utilisé pour évaluer l'activité basale des rongeurs (rats et...

Le nouveau Test de Nage Forcée Bioseb DUAL SENSOR à été développé selon une double approche: En...

Un nouveau système innovant pour l'automatisation du test de Reconnaissance d'Object ("Novel...

Test open-field - ARENE UNIQUEMENT utilisé pour évaluer l'activité basale des rongeurs (rats et...

Un système expérimental d'enclos entièrement modulable conçu pour conduire des procédures de...

Appareil d'utilisation très simple pour souris Possibilité de sortir les données sur PC

Une chambre expérimentale standard pour l'évaluation automatisée ou manuelle de la préférence de...
Mesures des paramètres physiologique en temps réel chez le rats - non invasive et sans aucune...

L'ETH-401 est un amplificateur de pont pour différents transducteurs qui fournit quatre canaux...

Le IX-118 est un système d'acquisition de données rapide 100 kHz à haute résolution et approprié...

L'ETH-256 est un amplificateur 2 canaux haute performance à usage général de la recherche en...

Stimulateur à canaux multiples toutes options pour stimulation neuro-musculaire

Découvrez BIO-FOODIS, la solution de nouvelle génération pour comprendre le comportement...

Système modulaire permettant l'intégration du métabolisme respiratoire, de l'apport de...

Équipements innovants et appropriés pour mesurer la consommation de nourriture / boisson ainsi...

Un analyseur d'oxygène et de dioxyde de carbone économique, de haute performance avec des taux...
Un algomètre rapide et précis, basé sur une pince instrumentée: une alternative au test de Randall-Selitto. Ce nouvel algésimètre développé par Bioseb selon Luis-Delgado et al. (2005) permet des tests nociceptifs précis et la mesure du seuil de douleur mécanique sur pattes de rats ou de souris, avec une contrainte minimale. Maintenant en version sans-fil, pour être libéré des câbles!
![]()
![]()
![]() Présentation
Présentation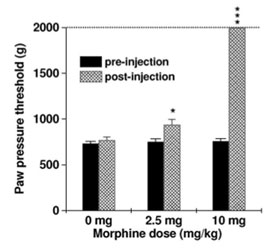 L’Algomètre à Pince Instrumentée pour Rongeurs de Bioseb permet, à l’aide d’un forceps calibré, d’induire une stimulation mécanique quantifiable sur un animal (rat ou souris) sur une échelle linéaire. Le protocole optimal a été défini expérimentalement en déterminant les effets de 3 meures répétitives sur les 2 pattes arrières, respectivement sur le long terme (9 jours), le moyen terme (1 jour) et le court terme (2 heures). Cet instrument a été développé à l’origine en tant qu’algésimètre/algomètre (instrument de mesure de l’analgésie, ou analgésimètre) pour les tests nociceptifs. Pour cet usage spécifique, il constitue une alternative au test de “RANDALL & SELITTO” - mais présente les avantages suivants comparé au test classique :
L’Algomètre à Pince Instrumentée pour Rongeurs de Bioseb permet, à l’aide d’un forceps calibré, d’induire une stimulation mécanique quantifiable sur un animal (rat ou souris) sur une échelle linéaire. Le protocole optimal a été défini expérimentalement en déterminant les effets de 3 meures répétitives sur les 2 pattes arrières, respectivement sur le long terme (9 jours), le moyen terme (1 jour) et le court terme (2 heures). Cet instrument a été développé à l’origine en tant qu’algésimètre/algomètre (instrument de mesure de l’analgésie, ou analgésimètre) pour les tests nociceptifs. Pour cet usage spécifique, il constitue une alternative au test de “RANDALL & SELITTO” - mais présente les avantages suivants comparé au test classique :
• Manipulation plus éthique, moins stressante pour l’animal (rat ou souris), résultant en des mesures moins variables
• Mesures plus rapides, moins traumatisantes pour les tissus
• Mesure digitalisée avec traçabilité métrologique
Cependant, cet algésimètre basé sur une pince peut également être utilisé pour d’autres applications nécessitant une valeur de force ou de pression contrôlée, comme par exemple :
• Récupération sensitive après l’écrasement d’un nerf: le pincement est appliqué en différents endroits de la patte pour vérifier la récupération sensitive
• Blessures mécaniques pour les modèles thrombotiques
• Stimulation mécanique pour les enregistrements électrophysiologiques in-vivo utilisant les possibilités de déclenchement de l’enregistrement par seuil de force
Des études comparatives (incluant des tests comparatifs avec l’algésimètre de Randall & Sellito) ont démontré la précision de cet algésimètre à pince pour des mesures rapides, simples et reproductibles du seuil de douleur mécanique des membres de rat. De plus, l'algomètre à pince instrumentée permet de de procéder à des tests analgésiques sur rat avaec un niveau de contrainte minimum, réduisant la variabilité des données.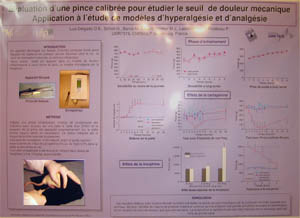
 L’un de ces travaux de recherche expérimentale a été effectué par l’équipe du Prof. Poisbeau au département de 'Nociception & Douleur' de 'l’Institut des Neurosciences Cellulaires et Intégratives' (Université Louis pasteur) de Strasbourg.
L’un de ces travaux de recherche expérimentale a été effectué par l’équipe du Prof. Poisbeau au département de 'Nociception & Douleur' de 'l’Institut des Neurosciences Cellulaires et Intégratives' (Université Louis pasteur) de Strasbourg.
Ces travaux ont été décrits dans 2 articles publiés dans des revues scientifiques internationales à comité de lecture :
• Méthode de validation :
Calibrated Forceps: A Sensitive and Reliable Tool for Pain and Analgesia Studies, by Luis-Delgado et al. in The Journal of pain, Décembre 2005
• Travail scientifique :
Inflammatory Pain Upregulates Spinal Inhibition via Endogenous Neurosteroid Production, by P. Poisbeau et al. in The Journal of neuroscience, Décembre 2005

![]() NOUVEAU: Sans fil
NOUVEAU: Sans fil
Une gamme complète d'instruments Bioseb, incluant la pince instrumentée, comprend désormais notre nouvelle technologie sans fil: grâce au boîtier sans fi placé sur le poignet de l'opérateur, il n'y a plus de câble entre la console éléctronique de l'écran et les capteurs
Cette nouvelle technologie sans fil offre de nombreux avantages:
• Mailleure liberté de mouvement: plus de câbes agaçants !
• Une configuration flexible pour votre laboratoire : concevez votre espace de travail sans limites
• Libérez vous des contraintes physiques : concentrez vous sur votre expérience !
![]() Fourni avec: Composants inclus
Fourni avec: Composants inclus
Ces composants intégrés facilitent les mesures analgésiques:
• Bâti de bureau pour une lecture facile
• Pédale pour le tarage “main libre” de l’analgésimètre à pince pour rongeurs au démarrage
• Sortie RS232 pour le transfert des données à un PC
• Notre nouveau design de pince permet le montage d’embouts personnalisés pour répondre à vos applications analgésiques les plus spécifiques. Merci de nous contacter si vous avez une requête spéciale concernant la pince, et nous ferons de notre mieux pour la satisfaire.
L'algomètre à pince instrumentée pour rongeurs de Bioseb est founi avec : unité de contrôle électronique (avec batteries et adaptateur secteur) ; une pince pour rat ou souris d’une capacité de 2000 grammes ; une mallette de transport ; une pédale pour tarage de la force “main-libre” ; une sortie RS232 ; un manuel d’utilisation![]() Options
Options
• Notre logiciel Bio-CIS2 en option (pour Windows) envoit les valeurs affichées directement dans une feuille de calculs Excel. Cela permet d’obtenir immédiatement un rapport pour analyse supplémentaire, sans erreurs de recopie. Fourni avec un câble RS-232.
• Module externe pour allumer une diode rouge ou émettre un son lorsqu’un seuil de force prédéfini a été atteint.
• Sortie analogique et câble.
• Sortie TTL
• Tests et capteurs aditionnels : notre sonde de Test de Von Frey Electronique et notre Algomètre pour Petit Animal sont fournis avec leurs propres modules de calibration qui sont reconnus par l’unité élecronique de la Pince Instrumentée.![]() Nouveau système AlgoKit
Nouveau système AlgoKit
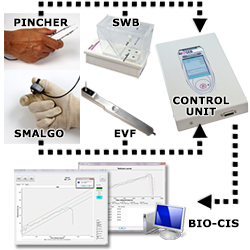
Vous pouvez également être intéressé par notre nouveau système ALGOKIT afin d'étendre le champs des possibles pour vos recherches. Pour répondre aux diverses demandes concernant les différents cas possibles en mesure de la douleur et pour faire face à toutes les situations, Bioseb est fière de présenter l'AlgoKit construit autour de notre test d'Incapacitance Statique (SWB: Distribution Pondérale Statique), avec son écran tactile couleurs, et de jusqu'à 3 capteurs additionnels parmi notreVon Frey Électronique, de la Pince Instrumentée et de l'algomètre pour petits animaux (SMALGO) combinés à un unique boitier de contrôle ! .
Avantages:
• Flexibilité : solution complète pour les mesure d’analgésie à portée de main !
• Compatible avec le logiciel d'acquisition BIO-CIS2 pour améliorer la répétabilité des tests nociceptifs.
Fiche technique
Array
(
[2110] => Array
(
[id] => 2110
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Sex-specific-spatial-memory-deficits-associated-with-region-specific-neuroinflammatory-changes-in-the-dorsal-hippocampus-of-rats-exposed-to-neonatal-repeated-maternal-separation-n2110
[title] => Sex-specific spatial memory deficits associated with region-specific neuroinflammatory changes in the dorsal hippocampus of rats exposed to neonatal repeated maternal separation
[paragraph_crop] => Sex-specific spatial memory deficits associated with region-specific neuroinflammatory changes [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-10-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2105] => Array
(
[id] => 2105
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Psilocybin-has-no-immediate-or-persistent-analgesic-effect-in-acute-and-chronic-mouse-pain-models-n2105
[title] => Psilocybin has no immediate or persistent analgesic effect in acute and chronic mouse pain models
[paragraph_crop] => Psilocybin has no immediate or persistent analgesic effect in acute and chronic mouse pain models
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-07-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2107] => Array
(
[id] => 2107
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Blockade-of-IgG-Fc-receptors-reduces-pain-after-intervertebral-disc-injury-n2107
[title] => Blockade of IgG Fc receptors reduces pain after intervertebral disc injury
[paragraph_crop] => Blockade of IgG Fc receptors reduces pain after intervertebral disc injury
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-06-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2109] => Array
(
[id] => 2109
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Lung-specific-SFTPC-mutations-lead-to-neurodevelopmental-disorders-with-neuroinflammation-n2109
[title] => Lung-specific SFTPC mutations lead to neurodevelopmental disorders with neuroinflammation
[paragraph_crop] => Lung-specific SFTPC mutations lead to neurodevelopmental disorders with neuroinflammation
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-03-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[43] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 43
[title] => Neurodégénérescences générales
[link_rewrite] => Neurodegenerescences-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2106] => Array
(
[id] => 2106
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Aβ-low-threshold-mechanoreceptors-contribute-to-sensory-abnormalities-in-fibromyalgia-n2106
[title] => Aβ low threshold mechanoreceptors contribute to sensory abnormalities in fibromyalgia
[paragraph_crop] => Aβ low threshold mechanoreceptors contribute to sensory abnormalities in fibromyalgia
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2108] => Array
(
[id] => 2108
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Characterisation-of-the-effects-of-the-chemotherapeutic-agent-paclitaxel-on-neuropathic-pain-related-behaviour--anxiodepressive-behaviour--cognition--and-the-endocannabinoid-system-in-male-and-female-rats-n2108
[title] => Characterisation of the effects of the chemotherapeutic agent paclitaxel on neuropathic pain-related behaviour- anxiodepressive behaviour- cognition- and the endocannabinoid system in male and female rats
[paragraph_crop] => Characterisation of the effects of the chemotherapeutic agent paclitaxel on neuropathic [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-01-03 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1892] => Array
(
[id] => 1892
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/par2-dependent-phosphorylation-of-trpv4-at-the-trigeminal-nerve-terminals-contributes-to-tongue-cancer-pain-n1892
[title] => PAR2-dependent phosphorylation of TRPV4 at the trigeminal nerve terminals contributes to tongue cancer pain
[paragraph_crop] => PAR2-dependent phosphorylation of TRPV4 at the trigeminal nerve terminals contributes to [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-12-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[31] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 31
[title] => Douleurs oro-faciales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-oro-faciales
)
)
)
[1923] => Array
(
[id] => 1923
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/m2-macrophage-derived-cathepsin-s-promotes-peripheral-nerve-regeneration-via-fibroblast-schwann-cell-signaling-relay-n1923
[title] => M2 macrophage-derived cathepsin S promotes peripheral nerve regeneration via fibroblast-Schwann cell-signaling relay
[paragraph_crop] => M2 macrophage-derived cathepsin S promotes peripheral nerve regeneration via [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-11-09 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
)
)
[1895] => Array
(
[id] => 1895
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/rta-408-regulates-p-nf-b-and-tslp-and-stat5-signaling-to-ameliorate-nociceptive-hypersensitivity-in-chronic-constriction-injury-rats-n1895
[title] => RTA-408 Regulates p-NF-κB and TSLP and STAT5 Signaling to Ameliorate Nociceptive Hypersensitivity in Chronic Constriction Injury Rats
[paragraph_crop] => RTA-408 Regulates p-NF-κB and TSLP and STAT5 Signaling to Ameliorate Nociceptive [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-09-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1517] => Array
(
[id] => 1517
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-novel-analgesic-pathway-from-parvocellular-oxytocin-neurons-to-the-periaqueductal-gray-n1517
[title] => A novel analgesic pathway from parvocellular oxytocin neurons to the periaqueductal gray
[paragraph_crop] => A novel analgesic pathway from parvocellular oxytocin neurons to the periaqueductal gray
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-02-24 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1509] => Array
(
[id] => 1509
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-contribution-of-tslp-activation-to-hyperalgesia-in-dorsal-root-ganglia-neurons-of-a-rat-n1509
[title] => The Contribution of TSLP Activation to Hyperalgesia in Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons of a Rat
[paragraph_crop] => The Contribution of TSLP Activation to Hyperalgesia in Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons of a Rat
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-02-11 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1425] => Array
(
[id] => 1425
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/in-vivoecalcium-imaging-visualizes-incision-induced-primary-afferent-sensitization-and-its-amelioration-by-capsaicin-pretreatment-n1425
[title] => In VivoÊCalcium Imaging Visualizes Incision-Induced Primary Afferent Sensitization and Its Amelioration by Capsaicin Pretreatment
[paragraph_crop] => In VivoÊCalcium Imaging Visualizes Incision-Induced Primary Afferent Sensitization and Its [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-10-13 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1411] => Array
(
[id] => 1411
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inhibition-of-endothelin-a-receptor-by-a-novel--selective-receptor-antagonist-enhances-morphine-induced-analgesia--possible-functional-interaction-of-dimerized-endothelin-a-and-mu-opioid-receptors-n1411
[title] => Inhibition of endothelin A receptor by a novel- selective receptor antagonist enhances morphine-induced analgesia- Possible functional interaction of dimerized endothelin A and mu-opioid receptors
[paragraph_crop] => Inhibition of endothelin A receptor by a novel- selective receptor antagonist enhances [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1419] => Array
(
[id] => 1419
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/trpv1-blocker-hcrg21-suppresses-tnf-alpha-production-and-prevents-the-development-of-edema-and-hypersensitivity-in-carrageenan-induced-acute-local-inflammation-n1419
[title] => TRPV1 Blocker HCRG21 Suppresses TNF-alpha Production and Prevents the Development of Edema and hypersensitivity in Carrageenan-Induced Acute Local Inflammation
[paragraph_crop] => TRPV1 Blocker HCRG21 Suppresses TNF-alpha Production and Prevents the Development of Edema and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-06-23 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1402] => Array
(
[id] => 1402
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/linalool-odorinduced-analgesia-is-triggered-by-trpa1-independent-pathway-in-mice-n1402
[title] => Linalool odor_induced analgesia is triggered by TRPA1-independent pathway in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Linalool odor_induced analgesia is triggered by TRPA1-independent pathway in mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-04-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[51] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 51
[title] => Système somatosensoriel
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-somatosensoriel
)
)
)
[1398] => Array
(
[id] => 1398
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/methylmercury-induces-hyperalgesia-and-allodynia-through-spinal-cord-dorsal-horn-neuronal-activation-and-subsequent-somatosensory-cortical-circuit-formation-in-rats-n1398
[title] => Methylmercury induces hyperalgesia and allodynia through spinal cord dorsal horn neuronal activation and subsequent somatosensory cortical circuit formation in rats
[paragraph_crop] => Methylmercury induces hyperalgesia and allodynia through spinal cord dorsal horn neuronal [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-04-13 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1392] => Array
(
[id] => 1392
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/impact-of-hepatoma-derived-growth-factor-blockade-on-resiniferatoxin-induced-neuropathy-n1392
[title] => Impact of Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor Blockade on Resiniferatoxin-Induced Neuropathy
[paragraph_crop] => Impact of Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor Blockade on Resiniferatoxin-Induced Neuropathy
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-02-28 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1360] => Array
(
[id] => 1360
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/anti-inflammatory-and-analgesic-effects-of-trpv1-polypeptide-modulator-aphc3-in-models-of-osteo-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-n1360
[title] => Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of TRPV1 Polypeptide Modulator APHC3 in Models of Osteo-and Rheumatoid Arthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of TRPV1 Polypeptide Modulator APHC3 in Models of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-01-17 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1369] => Array
(
[id] => 1369
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/overexpression-of-chloride-importer-nkcc1-contributes-to-the-sensory-affective-and-sociability-phenotype-of-rats-following-neonatal-maternal-separation-n1369
[title] => Overexpression of chloride importer NKCC1 contributes to the sensory-affective and sociability phenotype of rats following neonatal maternal separation
[paragraph_crop] => Overexpression of chloride importer NKCC1 contributes to the sensory-affective and sociability [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-12-11 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[56] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 56
[title] => Anxiété
[link_rewrite] => Anxiété
)
[35] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 35
[title] => Douleurs émotionnelles
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-émotionnelles
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1272] => Array
(
[id] => 1272
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/neuropathic-pain-causes-a-decrease-in-the-dendritic-tree-complexity-of-hippocampal-ca3-pyramidal-neurons-n1272
[title] => Neuropathic Pain Causes a Decrease in the Dendritic Tree Complexity of Hippocampal CA3 Pyramidal Neurons
[paragraph_crop] => Neuropathic Pain Causes a Decrease in the Dendritic Tree Complexity of Hippocampal CA3 [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-07-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
)
)
[1235] => Array
(
[id] => 1235
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/oxytocin-acts-on-astrocytes-in-the-central-amygdala-to-promote-a-positive-emotional-state-n1235
[title] => Oxytocin Acts on Astrocytes in the Central Amygdala to Promote a Positive Emotional State
[paragraph_crop] => Oxytocin Acts on Astrocytes in the Central Amygdala to Promote a Positive Emotional State
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-02-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[56] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 56
[title] => Anxiété
[link_rewrite] => Anxiété
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[15] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 15
[title] => Troubles de l'humeur
[link_rewrite] => Troubles-de-l-humeur
)
)
)
[1234] => Array
(
[id] => 1234
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-nonpeptide-oxytocin-receptor-agonist-for-a-durable-relief-of-inflammatory-pain-n1234
[title] => A Nonpeptide Oxytocin Receptor Agonist for a Durable Relief of Inflammatory Pain
[paragraph_crop] => A Nonpeptide Oxytocin Receptor Agonist for a Durable Relief of Inflammatory Pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-02-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1232] => Array
(
[id] => 1232
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/neuropathic-pain-causes-memory-deficits-and-dendrite-tree-morphology-changes-in-mouse-hippocampus-n1232
[title] => Neuropathic Pain Causes Memory Deficits and Dendrite Tree Morphology Changes in Mouse Hippocampus
[paragraph_crop] => Neuropathic Pain Causes Memory Deficits and Dendrite Tree Morphology Changes in Mouse Hippocampus
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-02-11 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1189] => Array
(
[id] => 1189
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/bioscreening-of-the-spacerized-complex-bis--2-pyridyl--3--1--2--4-triazolyl--propane-and-11-hydroxy-1--1-ethylidenediphosphonic-acid-n1189
[title] => Bioscreening of the spacerized complex BIS -2-Pyridyl--3--1- 2- 4-Triazolyl- propane and 11-Hydroxy-1- 1-Ethylidenediphosphonic acid
[paragraph_crop] => Bioscreening of the spacerized complex BIS (2-Pyridyl)-3-(1, 2, 4-Triazolyl) propane and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-12-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
[94] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 94
[title] => Toxicologie
[link_rewrite] => Toxicologie
)
)
)
[1150] => Array
(
[id] => 1150
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/effect-of-1-hydroxy-1-1-ethylidendiphosphone-acid--bis-2-pyridyl-1-2-4-triazolyl-3-propane-and-their-adduct-on-the-pain-sensitivity-of-rats-pyridyl-1-2-4-triazolyl-3-propane-and-their-adduct-on-the-pain-sensitivity-of-rats-n1150
[title] => EFFECT OF 1-HYDROXY-1-1-ETHYLIDENDIPHOSPHONE ACID- BIS-2-PYRIDYL-1-2-4-TRIAZOLYL-3-PROPANE AND THEIR ADDUCT ON THE PAIN SENSITIVITY OF RATS PYRIDYL-1-2-4-TRIAZOLYL-3-PROPANE AND THEIR ADDUCT ON THE PAIN SENSITIVITY OF RATS
[paragraph_crop] => EFFECT OF 1-HYDROXY-1,1-ETHYLIDENDIPHOSPHONE ACID, BIS(2-PYRIDYL-1,2,4-TRIAZOLYL-3)PROPANE AND [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-08-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1156] => Array
(
[id] => 1156
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/effect-of-1-hydroxy-1-1-thylidendiphosphone-acid--bis-2-pyridyl-1-2-4-triazolyl-3-propane-and-their-adduct-on-the-pain-sensitivty-of-rats-n1156
[title] => Effect of 1-Hydroxy-1-1-thylidendiphosphone Acid- Bis-2-Pyridyl-1-2-4-Triazolyl-3-Propane and their adduct on the pain sensitivty of Rats
[paragraph_crop] => Effect of 1-Hydroxy-1,1-thylidendiphosphone Acid, Bis(2-Pyridyl-1,2,4-Triazolyl-3)Propane and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-07-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1163] => Array
(
[id] => 1163
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/influence-of-1-hydroxy-1-1-ethylidendiphosphone-acid-and-bis--2-pyridyl-1-2-4-triazolyl-3--propane-on-pain-sensitivity-of-rat-females-n1163
[title] => INFLUENCE OF 1-HYDROXY-1-1-ETHYLIDENDIPHOSPHONE ACID AND BIS -2-PYRIDYL-1-2-4-TRIAZOLYL-3- PROPANE ON PAIN SENSITIVITY OF RAT FEMALES
[paragraph_crop] => INFLUENCE OF 1-HYDROXY-1,1-ETHYLIDENDIPHOSPHONE ACID AND BIS (2-PYRIDYL-1,2,4-TRIAZOLYL-3) [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-07-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1123] => Array
(
[id] => 1123
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/cholecalciferol--vitamin-d-3--reduces-rat-neuropathic-pain-by-modulating-opioid-signaling-n1123
[title] => Cholecalciferol -Vitamin D 3- Reduces Rat Neuropathic Pain by Modulating Opioid Signaling
[paragraph_crop] => Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D 3) Reduces Rat Neuropathic Pain by Modulating Opioid Signaling
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-04-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1101] => Array
(
[id] => 1101
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/analgesic-and-anti-edemic-properties-of-etifoxine-in-models-of-inflammatory-sensitization-n1101
[title] => Analgesic and anti-edemic properties of etifoxine in models of inflammatory sensitization
[paragraph_crop] => Analgesic and anti-edemic properties of etifoxine in models of inflammatory sensitization
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-02-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[976] => Array
(
[id] => 976
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/sphingosine-1-phosphate-and-the-s1p3-receptor-initiate-neuronal-retraction-via-rhoa-and-rock-associated-with-crmp2-phosphorylation-n976
[title] => Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and the S1P3 Receptor Initiate Neuronal Retraction via RhoA and ROCK Associated with CRMP2 Phosphorylation
[paragraph_crop] => Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and the S1P3 Receptor Initiate Neuronal Retraction via RhoA/ROCK [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-10-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[1102] => Array
(
[id] => 1102
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/application-of-calibrated-forceps-for-assessing-mechanical-nociception-with-high-time-resolution-in-mice-n1102
[title] => Application of calibrated forceps for assessing mechanical nociception with high time resolution in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Application of calibrated forceps for assessing mechanical nociception with high time [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-02-17 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[842] => Array
(
[id] => 842
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/anti-nociceptive-properties-of-shikonin--in-vitro-and-in-vivo-studies-n842
[title] => Anti-nociceptive properties of shikonin- In vitro and In vivo studies
[paragraph_crop] => Anti-nociceptive properties of shikonin: In vitro and In vivo studies
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2016-07-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[839] => Array
(
[id] => 839
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-new-population-of-parvocellular-oxytocin-neurons-controlling-magnocellular-neuron-activity-and-inflammatory-pain-processing-n839
[title] => A New Population of Parvocellular Oxytocin Neurons Controlling Magnocellular Neuron Activity and Inflammatory Pain Processing
[paragraph_crop] => A New Population of Parvocellular Oxytocin Neurons Controlling Magnocellular Neuron Activity [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2016-03-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[748] => Array
(
[id] => 748
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/pharmacodynamic-evaluation-of-sustained-release-of-peg-and-pla-formulation-including-bupivacane-or-ropivacane-versus-0-25-bupivacane-after-sciatic-nerve-block-in-rat-n748
[title] => Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of Sustained Release of PEG and PLA Formulation Including Bupivacaïne or Ropivacaïne versus 0-25% Bupivacaïne After Sciatic Nerve Block in Rat
[paragraph_crop] => Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of Sustained Release of PEG/PLA Formulation Including Bupivacaïne [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-10-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[95] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 95
[title] => Pharmacologie
[link_rewrite] => Pharmacologie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[753] => Array
(
[id] => 753
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/long-term-behavioral-effects-in-a-rat-model-of-prolonged-postnatal-morphine-exposure--n753
[title] => Long-Term Behavioral Effects in a Rat Model of Prolonged Postnatal Morphine Exposure-
[paragraph_crop] => Long-Term Behavioral Effects in a Rat Model of Prolonged Postnatal Morphine Exposure.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-10-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[805] => Array
(
[id] => 805
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/en3427--a-novel-cationic-aminoindane-with-long-acting-local-anesthetic-properties-n805
[title] => EN3427- A Novel Cationic Aminoindane with Long-Acting Local Anesthetic Properties
[paragraph_crop] => EN3427: A Novel Cationic Aminoindane with Long-Acting Local Anesthetic Properties
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-04-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[678] => Array
(
[id] => 678
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/corticosterone-analgesia-is-mediated-by-the-spinal-production-of-neuroactive-metabolites-that-enhance-gabaergic-inhibitory-transmission-on-dorsal-horn-rat-neurons-n678
[title] => Corticosterone analgesia is mediated by the spinal production of neuroactive metabolites that enhance GABAergic inhibitory transmission on dorsal horn rat neurons
[paragraph_crop] => Corticosterone analgesia is mediated by the spinal production of neuroactive metabolites that [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[664] => Array
(
[id] => 664
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/characterization-of-the-fast-gabaergic-inhibitory-action-of-etifoxine-during-spinal-nociceptive-processing-in-male-rats-n664
[title] => Characterization of the fast GABAergic inhibitory action of etifoxine during spinal nociceptive processing in male rats
[paragraph_crop] => Characterization of the fast GABAergic inhibitory action of etifoxine during spinal [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-12-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[706] => Array
(
[id] => 706
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/peripheral-nerve-regeneration-and-ngf-dependent-neurite-outgrowth-of-adult-sensory-neurons-converge-on-stat3-phosphorylation-downstream-of-neuropoietic-cytokine-receptor-gp130--n706
[title] => Peripheral nerve regeneration and NGF-dependent neurite outgrowth of adult sensory neurons converge on STAT3 phosphorylation downstream of neuropoietic cytokine receptor gp130-
[paragraph_crop] => Peripheral nerve regeneration and NGF-dependent neurite outgrowth of adult sensory neurons [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-09-24 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[568] => Array
(
[id] => 568
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/plasma-glucocorticoids-differentially-modulate-phasic-and-tonic-gaba-inhibition-during-early-postnatal-development-in-rat-spinal-lamina-ii-n568
[title] => Plasma glucocorticoids differentially modulate phasic and tonic GABA inhibition during early postnatal development in rat spinal lamina II
[paragraph_crop] => Plasma glucocorticoids differentially modulate phasic and tonic GABA inhibition during early [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-06-23 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[502] => Array
(
[id] => 502
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/feasibility-and-repeatability-of-cold-and-mechanical-quantitative-sensory-testing-in-normal-dogs-n502
[title] => Feasibility and repeatability of cold and mechanical quantitative sensory testing in normal dogs
[paragraph_crop] => Feasibility and repeatability of cold and mechanical quantitative sensory testing in normal dogs
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-10-28 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[506] => Array
(
[id] => 506
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/long-lasting-spinal-oxytocin-analgesia-is-ensured-by-the-stimulation-of-allopregnanolone-synthesis-which-potentiates-gabaa-receptor-mediated-synaptic-inhibition--n506
[title] => Long-Lasting Spinal Oxytocin Analgesia Is Ensured by the Stimulation of Allopregnanolone Synthesis Which Potentiates GABAA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Inhibition
[paragraph_crop] => Long-Lasting Spinal Oxytocin Analgesia Is Ensured by the Stimulation of Allopregnanolone [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-10-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[48] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 48
[title] => Perception du chaud et du froid
[link_rewrite] => Perception-du-chaud-et-du-froid
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[13] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 13
[title] => Système sensoriel
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-sensoriel
)
)
)
[545] => Array
(
[id] => 545
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/etifoxine-stimulates-allopregnanolone-synthesis-in-the-spinal-cord-to-produce-analgesia-in-experimental-mononeuropathy-n545
[title] => Etifoxine stimulates allopregnanolone synthesis in the spinal cord to produce analgesia in experimental mononeuropathy
[paragraph_crop] => Etifoxine stimulates allopregnanolone synthesis in the spinal cord to produce analgesia in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-07-24 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[473] => Array
(
[id] => 473
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/phenotyping-the-function-of-trpv1-expressing-sensory-neurons-by-targeted-axonal-silencing--n473
[title] => Phenotyping the function of TRPV1-expressing sensory neurons by targeted axonal silencing-
[paragraph_crop] => Phenotyping the function of TRPV1-expressing sensory neurons by targeted axonal silencing.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-01-02 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[447] => Array
(
[id] => 447
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/long-term-changes-in-trigeminal-ganglionic-and-thalamic-neuronal-activities-following-inferior-alveolar-nerve-transection-in-behaving-rats--n447
[title] => Long-Term Changes in Trigeminal Ganglionic and Thalamic Neuronal Activities following Inferior Alveolar Nerve Transection in Behaving Rats
[paragraph_crop] => Long-Term Changes in Trigeminal Ganglionic and Thalamic Neuronal Activities following Inferior [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-11-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[31] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 31
[title] => Douleurs oro-faciales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-oro-faciales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[481] => Array
(
[id] => 481
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/effects-of-peripheral-inflammation-on-the-blood-spinal-cord-barrier-n481
[title] => Effects of peripheral inflammation on the blood spinal cord barrier
[paragraph_crop] => Effects of peripheral inflammation on the blood spinal cord barrier
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-06-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[354] => Array
(
[id] => 354
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/erythropoietin-restores-c-fiber-function-and-prevents-pressure-ulcer-formation-in-diabetic-mice---n354
[title] => Erythropoietin Restores C-Fiber Function and Prevents Pressure Ulcer Formation in Diabetic Mice-
[paragraph_crop] => Erythropoietin Restores C-Fiber Function and Prevents Pressure Ulcer Formation in Diabetic Mice.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-11-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[350] => Array
(
[id] => 350
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/endogenous-opioids-released-during-non-nociceptive-environmental-stress-induce-latent-pain-sensitization-via-a-nmda-dependent-process---n350
[title] => Endogenous Opioids Released During Non-Nociceptive Environmental Stress Induce Latent Pain Sensitization Via a NMDA-Dependent Process-
[paragraph_crop] => Endogenous Opioids Released During Non-Nociceptive Environmental Stress Induce Latent Pain [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-10-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[328] => Array
(
[id] => 328
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/evidence-for-a-differential-opioidergic-involvement-in-the-analgesic-effect-of-antidepressants--prediction-for-efficacy-in-animal-models-of-neuropathic-pain--n328
[title] => Evidence for a differential opioidergic involvement in the analgesic effect of antidepressants- prediction for efficacy in animal models of neuropathic pain?
[paragraph_crop] => Evidence for a differential opioidergic involvement in the analgesic effect of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-06-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[293] => Array
(
[id] => 293
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-rat-intervertebral-disk-degeneration-pain-model--relationships-between-biological-and-structural-alterations-and-pain---n293
[title] => The rat intervertebral disk degeneration pain model- relationships between biological and structural alterations and pain-
[paragraph_crop] => The rat intervertebral disk degeneration pain model: relationships between biological and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-05-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[72] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 72
[title] => Bas dos & disques
[link_rewrite] => Bas-dos-disques
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[301] => Array
(
[id] => 301
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/phosphorylation-of-spinal-n-methyl-d-aspartate-receptor-nr1-subunits-by-extracellular-signal-regulated-kinase-in-dorsal-horn-neurons-and-microglia-contributes-to-diabetes-induced-painful-neuropathy---n301
[title] => Phosphorylation of spinal N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor NR1 subunits by extracellular signal-regulated kinase in dorsal horn neurons and microglia contributes to diabetes-induced painful neuropathy-
[paragraph_crop] => Phosphorylation of spinal N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor NR1 subunits by extracellular [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[285] => Array
(
[id] => 285
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/magnesium-attenuates-chronic-hypersensitivity-and-spinal-cord-nmda-receptor-phosphorylation-in-a-rat-model-of-diabetic-neuropathic-pain---n285
[title] => Magnesium attenuates chronic hypersensitivity and spinal cord NMDA receptor phosphorylation in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Magnesium attenuates chronic hypersensitivity and spinal cord NMDA receptor phosphorylation in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2010-11-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[250] => Array
(
[id] => 250
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/differential-anti-neuropathic-pain-effects-of-tetrodotoxin-in-sciatic-nerve--versus-infraorbital-nerve-ligated-rats--behavioral--pharmacological-and-immunohistochemical-investigations---n250
[title] => Differential anti-neuropathic pain effects of tetrodotoxin in sciatic nerve- versus infraorbital nerve-ligated rats – Behavioral- pharmacological and immunohistochemical investigations-
[paragraph_crop] => Differential anti-neuropathic pain effects of tetrodotoxin in sciatic nerve- versus [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2010-02-28 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[244] => Array
(
[id] => 244
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/reduction-and-prevention-of-vincristine-induced-neuropathic-pain-symptoms-by-the-non-benzodiazepine-anxiolytic-etifoxine-are-mediated-by-3-reduced-neurosteroids--n244
[title] => Reduction and prevention of vincristine-induced neuropathic pain symptoms by the non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic etifoxine are mediated by 3_-reduced neurosteroids-
[paragraph_crop] => Reduction and prevention of vincristine-induced neuropathic pain symptoms by the [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2009-12-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[241] => Array
(
[id] => 241
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/increase-in-morphine-antinociceptive-activity-by-a-p-glycoprotein-inhibitor-in-cisplatin-induced-neuropathy--n241
[title] => Increase in morphine antinociceptive activity by a P-glycoprotein inhibitor in cisplatin-induced neuropathy-
[paragraph_crop] => Increase in morphine antinociceptive activity by a P-glycoprotein inhibitor in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2009-11-06 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[199] => Array
(
[id] => 199
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/combination-of-microsurgery-and-gene-therapy-for-spinal-dorsal-root-injury-repair--n199
[title] => Combination of Microsurgery and Gene Therapy for Spinal Dorsal Root Injury Repair-
[paragraph_crop] => Combination of Microsurgery and Gene Therapy for Spinal Dorsal Root Injury Repair.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2009-06-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[179] => Array
(
[id] => 179
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/fast-non-genomic-effects-of-progesterone-derived-neurosteroids-on-nociceptive-thresholds-and-pain-symptoms--n179
[title] => Fast non-genomic effects of progesterone-derived neurosteroids on nociceptive thresholds and pain symptoms-
[paragraph_crop] => Fast non-genomic effects of progesterone-derived neurosteroids on nociceptive thresholds and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2008-10-31 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[170] => Array
(
[id] => 170
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/specific-antinociceptive-activity-of-cholest-4-en-3-one--oxime--tro19622--in-experimental-models-of-painful-diabetic-and-chemotherapy-induced-neuropathy--n170
[title] => Specific Antinociceptive Activity of Cholest-4-en-3-one- Oxime -TRO19622- in Experimental Models of Painful Diabetic and Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathy-
[paragraph_crop] => Specific Antinociceptive Activity of Cholest-4-en-3-one, Oxime (TRO19622) in Experimental [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2008-08-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[120] => Array
(
[id] => 120
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/mechanical--thermal-and-formalin-induced-nociception-is-differentially-altered-in-5-ht1a-and---5-ht1b-and---5-ht2a-and---5-ht3a-and--and-5-htt-and--knock-out-male-mice--n120
[title] => Mechanical- thermal and formalin-induced nociception is differentially altered in 5-HT1A_ and _- 5-HT1B_ and _- 5-HT2A_ and _- 5-HT3A_ and _ and 5-HTT_ and _ knock-out male mice-
[paragraph_crop] => Mechanical, thermal and formalin-induced nociception is differentially altered in 5-HT1A_/_, [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2007-08-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[117] => Array
(
[id] => 117
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/antinociceptive-efficacy-of-lacosamide-in-rat-models-for-tumor--and-chemotherapy-induced-cancer-pain--n117
[title] => Antinociceptive efficacy of lacosamide in rat models for tumor- and chemotherapy-induced cancer pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Antinociceptive efficacy of lacosamide in rat models for tumor- and chemotherapy-induced [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2007-06-22 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[116] => Array
(
[id] => 116
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/agmatine-induces-antihyperalgesic-effects-in-diabetic-rats-and-a-superadditive-interaction-with-r---3--2-carboxypiperazine-4-yl--propyl-1-phosphonic-acid--a-n-methyl-d-aspartate-receptor-antagonist--n116
[title] => Agmatine Induces Antihyperalgesic Effects in Diabetic Rats and a Superadditive Interaction with R-–--3--2-Carboxypiperazine-4-yl--propyl-1-phosphonic Acid- a N-Methyl-d-aspartate-Receptor Antagonist-
[paragraph_crop] => Agmatine Induces Antihyperalgesic Effects in Diabetic Rats and a Superadditive Interaction [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2007-06-05 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[106] => Array
(
[id] => 106
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/lacosamide--a-review-of-preclinical-properties--n106
[title] => Lacosamide- A Review of Preclinical Properties-
[paragraph_crop] => Lacosamide: A Review of Preclinical Properties.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2007-03-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[83] => Array
(
[id] => 83
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-transcription-factor-fosb-is-recruited-by-inflammatory-pain--n83
[title] => The transcription factor _FosB is recruited by inflammatory pain-
[paragraph_crop] => The transcription factor _FosB is recruited by inflammatory pain.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2006-09-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[79] => Array
(
[id] => 79
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/antinociceptive-efficacy-of-lacosamide-in-a-rat-model-for-painful-diabetic-neuropathy--n79
[title] => Antinociceptive efficacy of lacosamide in a rat model for painful diabetic neuropathy-
[paragraph_crop] => Antinociceptive efficacy of lacosamide in a rat model for painful diabetic neuropathy.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2006-06-06 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[70] => Array
(
[id] => 70
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/calibrated-forceps--a-sensitive-and-reliable-tool-for-pain-and-analgesia-studies--n70
[title] => Calibrated Forceps- A Sensitive and Reliable Tool for Pain and Analgesia Studies-
[paragraph_crop] => Calibrated Forceps: A Sensitive and Reliable Tool for Pain and Analgesia Studies.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2006-01-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[62] => Array
(
[id] => 62
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inflammatory-pain-upregulates-spinal-inhibition-via-endogenous-neurosteroid-production--n62
[title] => Inflammatory Pain Upregulates Spinal Inhibition via Endogenous Neurosteroid Production-
[paragraph_crop] => Inflammatory Pain Upregulates Spinal Inhibition via Endogenous Neurosteroid Production.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2005-12-14 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[48] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 48
[title] => Perception du chaud et du froid
[link_rewrite] => Perception-du-chaud-et-du-froid
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[13] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 13
[title] => Système sensoriel
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-sensoriel
)
)
)
)
1Nombre de publications:
Une solution rapide pour déterminer le seuil de sensibilité à la douleur mécanique chez les rongeurs (rats et souris).
En tant que version électronique du classique esthésiomètre à filaments de Von Frey, la dernière évolution de...
Nouvelles cage de contention modulables ROBUSTES pour maintenir doucement les rongeurs (rats et souris) durant les...
check_circle
check_circle